Cardiac Tests
Cardiac
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
It is routinely utilized in the initial diagnosis of many cardiac diseases and allows the detection of enlargements of the cardiac cavities, alterations in heart rhythm.
What conditions can be detected?
Arrhythmia.
Cardiomyopathy.
Coronary artery disease.
Heart attack.
Heart failure.
Diseases of the heart valves.
Congenital heart defects.
It is a simple test that does not cause any discomfort and poses no risk to the patient. It is very useful in diagnosing various conditions.
- Resting Electrocardiogram
- Average signal Electrocardiogram
- Holter Electrocardiogram (24 and 48 hours) with 7 and 12 leads.
A Holter monitor is a device that continuously records heart rhythms. It is worn for 24 to 48 hours during normal activities.
- Event Monitor
- Carotid Doppler Ultrasound.
It is a cardiac evaluation that provides insights into blood circulation through the neck arteries (carotid arteries).
These arteries are located in the neck and supply blood to the brain.
Arterial Hypertension
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM)
This type of monitoring allows the analysis of blood pressure values throughout the day, with daily activities.
Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
Syncope
- Tilt Table Test
This is a non-invasive test that involves abruptly changing the patient’s position to try to evoke the symptoms for which the test is performed, usually with the goal of inducing syncope (fainting).
Exercise Test(Stress test)
This type of test is often requested in routine check-ups, in the presence of symptoms suggesting heart disease, or when engaging in high-intensity physical activity.
- Conventional Cardiovascular Exercise Test (on a treadmill or cycle ergometer)
- Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (with analysis of exhaled gases).
In which cases should an exercise test be performed?
Patients with chest pain, as it could be a heart disease.
Individuals with arterial hypertension. (High blood pressure)
People who experience shortness of breath during any type of effort.
Patients with slow pulse, palpitations, or general heart rhythm disorders.
People without an apparent disease but at risk of developing heart disease (diabetes, cholesterol, family history, etc.), as part of routine medical check-ups or before engaging in intense physical activity.
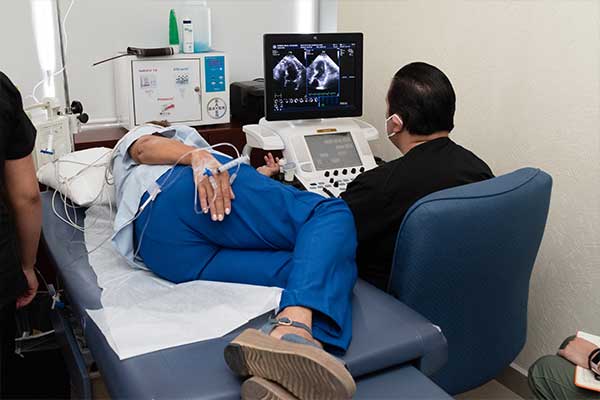
Echocardiogram (ECHO)
The echocardiogram is a fundamental diagnostic test that provides a heart-moving image. It involves visualizing the heart with an ultrasound while providing medication that prompts the heart to work more frequently and with more intensity, as if performing intense exercise.
It can also provide information on pulmonary circulation and pressures, the initial portion of the aorta, and check for fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion).
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram.
It is a fundamental diagnostic test because it provides a heart-moving image. Using ultrasound, echocardiography provides information about the shape, size, function, strength of the heart, movement and thickness of its walls, and the functioning of its valves.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram.
This test uses sound waves to produce an image of the heart and observe how it functions. Sound waves are sent through a tube inserted through the mouth and throat until reaching the esophagus (the part of the digestive tube that connects the throat to the stomach).
It is the most common type of echocardiogram. It does not cause pain or discomfort and involves externally placing the transducer on the chest wall to observe different parts of the heart.
- Echocardiogram with physical or pharmacological stress
Exercise or stress echocardiography allows us to evaluate how the heart behaves when subjected to physical stress, allowing, among other things, the determination of whether there is a part of the heart that is not receiving enough blood; for example, in the case of coronary artery disease.
The test involves alternately performing baseline echocardiography and physical stress on a treadmill and subsequently maximum stress echocardiography.
- Fetal Echocardiogram
Fetal echocardiography is an examination performed while the baby is still in the womb.
Generally, it is carried out during the second trimester of pregnancy, when the woman is approximately 18 to 24 weeks pregnant.
- Pediatric Echocardiogram
- Pediatric Transthoracic Echocardiogram
It is a diagnostic test performed on pediatric patients from newborns to an average age of 15 years.
- Fast Echocardiogram
Pulmonary
- 6-minute Walk Test
- Simple Spirometry
- Spirometry with bronchodilation
- Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (with analysis of exhaled gases).
It is a stress test similar to ergometry but much more comprehensive, as it includes measurement of variables such as oxygen saturation, ventilation per minute, and volumes of respiratory gases during exercise. It is widely used in high-performance athletes as well as in certain heart and respiratory diseases.
- Test for “Dyspnea” sensation (shortness of breath)
- Polysomnography
Sleep and Snoring Test (“Sleep Apnea”)
This test records certain bodily functions as one sleeps or tries to sleep. It is used to diagnose sleep disorders.
- Non-invasive Mechanical Ventilation Titration (“CPAP”)
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a designed and personalized program to improve the health of people with heart disease.
It helps to:
- Strengthen
- Reduce future risks of heart problems
- Prevent the heart condition from worsening
- Improve quality of life
Location
Privada Ignacio Zaragoza PTE # 16 II A Col. Centro.
Querétaro, Qro.
Phone
(442) 216 2745 y 46
(442) 242 5068
(442) 242-64-35
Instituto de Corazón de Querétaro 2018.
Instituto de Corazón de Querétaro 2018.
